INTRODUCTION
1 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
Exercises
2 DISEASES AND DISORDERS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
Exercises
3 DIABETES MELLITUS
Exercises
-----------------------
1-1. GENERAL
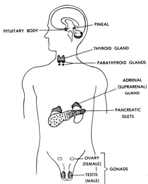
The endocrine system is one of two major systems which
control the body's activities. The endocrine system is composed of
glands which secrete substances called hormones into the bloodstream.
These hormones act as chemical messengers and float in the bloodstream
to the body's organs, the target of the particular hormone.
At the target, the hormone causes some action. The
hormone either turns on a biochemical reaction or turns off a
biochemical reaction.
a. The Endocrine System and the Nervous System.
The endocrine system works with the nervous system to regulate and
integrate the processes of the body such as growth, development,
reproduction, response to stress, and change of food into energy and
body tissue. The two systems work together like a giant super system.
Some parts of the nervous system stimulate or prevent
the release of hormones. Some hormones can stimulate or prevent
the flow of nerve impulses.
b. Composition and Activities of Hormones.
Hormones are composed of proteins, amino acids, or steroids. Although
hormones affect many of the body's activities, hormone actions can be
categorized into four broad areas:
(1) Internal environment control. Hormones help
control the body's internal environment by regulating the chemical
composition and volume of the body's fluids and tissues.
(2) Environmental condition adjustments. Hormones help
the body adjust to changes in the environment. Thanks to various
hormones, the body can cope with emergency demands such as infection,
trauma, emotional stress, dehydration, starvation, hemorrhage, and
temperature extremes.
(3) Growth and development. Hormones are instrumental
in regulating the growth and development of the body.
(4) Reproduction. Hormones are very important in the
basic process of reproduction. Various hormones play a significant
part in fertilization, nourishment of the embryo and fetus, delivery,
and nourishment of the newborn.
From The Endocrine System