MK3A2 Offensive Hand Grenade (Concussion Grenade)
|
Body: fiber, black in color with yellow markings. Weight 15.6 ounces Fuze Delay: 4-5 seconds Average soldier can throw it 40 meters. In open areas, effective casualty radius is 2 meters. In closed areas, the radius may be larger, due to overpressure effects. Secondary missiles and fuze pieces may be projected as far as 200 meters from the point of detonation. |
From Operational Medicine 2001: Health Care in Military Settings
CAPT Michael John Hughey, MC, USNR
NAVMED P-5139
January 1, 2001
Bureau of Medicine and
Surgery,
Department of the Navy,
2300 E Street NW,
Washington, D.C,
20372-5300
United States Special Operations Command,
7701 Tampa Point Blvd.,
MacDill AFB, Florida,
33621-5323
Home · Textbooks and Manuals · Videos · Lectures · Distance Learning · Training · Operational Safety · Search
This website is dedicated to the development and dissemination of medical information that may be useful to those who practice Operational Medicine. This website is privately-held and not connected to any governmental agency. The views expressed here are those of the authors, and unless otherwise noted, do not necessarily reflect the views of
the Brookside Associates, Ltd., any governmental or private organizations. All writings, discussions, and publications on this website are unclassified.
© 2006 Medical Education Division, Brookside Associates, Ltd. All rights reserved
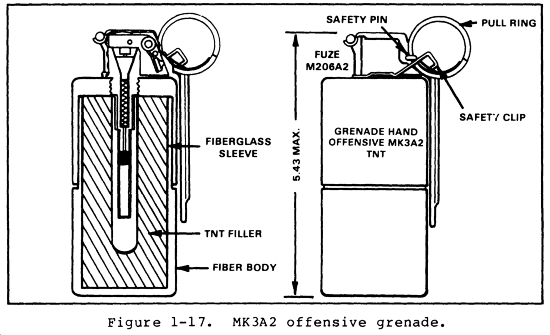 Used to produce casualties during close combat while minimizing
danger to friendly personnel. The grenade is also used for concussion
effects in enclosed areas, for blasting, or for demolition tasks. The
shock waves (overpressure) produced by this grenade when used in
enclosed areas are greater than those produced by the fragmentation
grenade. It is, therefore, very effective against enemy soldiers
located in bunkers, buildings, and fortified areas.
Used to produce casualties during close combat while minimizing
danger to friendly personnel. The grenade is also used for concussion
effects in enclosed areas, for blasting, or for demolition tasks. The
shock waves (overpressure) produced by this grenade when used in
enclosed areas are greater than those produced by the fragmentation
grenade. It is, therefore, very effective against enemy soldiers
located in bunkers, buildings, and fortified areas.