|
|
Operational Obstetrics & Gynecology
Yeast (Candida, Monilia)
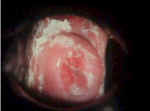
Vaginal yeast infections are common, monilial overgrowths in the vagina and vulvar areas, characterized by itching,dryness, and a thick, cottage-cheese appearing vaginal discharge. The vulva may be reddened and irritated to the point of tenderness.
These infections are particularly troublesome in operational settings where they are both frequent and annoying. Yeast thrives in damp, hot environments and women in such circumstances are predisposed toward these infections.Women who take broad-spectrum antibiotics are also predisposed towards these infections because of loss of the normal vaginal bacterial flora.
Yeast organisms are normally present in most vaginas, but in small numbers. A yeast infection, then, is not merely the presence of yeast, but the concentration of yeast in such large numbers as to cause the typical symptoms of itching, burning and discharge. Likewise, a "cure" doesn't mean eradication of all yeast organisms from the vagina. Even if eradicated, they would soon be back because that is where they normally live. A cure means that the concentration of yeast has been restored to normal and symptoms have resolved.
The diagnosis is often made by history alone, and enhanced by the classical appearance of a dry, cheesy vaginal discharge. It can be confirmed by microscopic visualization of clusters of thread-like, branching Monilia organisms when the discharge is mixed with KOH.
 Treatment consists of an oral antifungal agent,
Treatment consists of an oral antifungal agent,
- Fluconazole 150 mg oral tablet, one tablet in single dose,
or intravaginal agents:
- Butoconazole 2% cream 5 g intravaginally for 3 days
- Clotrimazole 1% cream 5 g intravaginally for 7-14 days
- Clotrimazole 100 mg vaginal tablet for 7 days
-
 Clotrimazole 100 mg vaginal tablet, two tablets for 3 days
Clotrimazole 100 mg vaginal tablet, two tablets for 3 days - Clotrimazole 500 mg vaginal tablet, one tablet in a single application
- Miconazole 2% cream 5 g intravaginally for 7 days
- Miconazole 200 mg vaginal suppository, one suppository for 3 days
- Miconazole 100 mg vaginal suppository, one suppository for 7 days
- Nystatin 100,000-unit vaginal tablet, one tablet for 14 days
- Tioconazole 6.5% ointment 5 g intravaginally in a single application
- Terconazole 0.4% cream 5 g intravaginally for 7 days
- Terconazole 0.8% cream 5 g intravaginally for 3 days
- Terconazole 80 mg vaginal suppository, one suppository for 3 days.
If none of these products are available, douching with a weak acid solution (2 teaspoons of vinegar in a quart of warm water) twice a day will help restore an acid pH to the vagina, inhibiting yeast proliferation. Stop douching when symptoms have resolved as the douche itself tends to remove some of the protective mucous within the vagina.
Whenever the skin of the vulva is involved, more frequent treatment for a longer period of time may be necessary.
Reoccurrences are common and can be treated the same as for initial infections. For chronic recurrences, many patients find the use of a single applicator of Monistat 7 at the onset of itching will abort the attack completely. Sexual partners need not be treated unless they are symptomatic.
Read more about wet mounts and yeast
Home · Introduction · Medical Support of Women in Field Environments · The Prisoner of War Experience · Routine Care · Pap Smears · Human Papilloma Virus · Contraception · Birth Control Pills · Vulvar Disease · Vaginal Discharge · Abnormal Bleeding · Menstrual Problems · Abdominal Pain · Urination Problems · Menopause · Breast Problems · Sexual Assault · Normal Pregnancy · Abnormal Pregnancy · Normal Labor and Delivery · Problems During Labor and Delivery · Care of the Newborn
|
Bureau of Medicine
and Surgery |
Operational
Obstetrics & Gynecology - 2nd Edition |
This web version of Operational Obstetrics & Gynecology is provided by The Brookside Associates Medical Education Division. It contains original contents from the official US Navy NAVMEDPUB 6300-2C, but has been reformatted for web access and includes advertising and links that were not present in the original version. This web version has not been approved by the Department of the Navy or the Department of Defense. The presence of any advertising on these pages does not constitute an endorsement of that product or service by either the Department of Defense or the Brookside Associates. The Brookside Associates is a private organization, not affiliated with the United States Department of Defense. All material in this version is unclassified.
This formatting © 2006
Medical Education Division,
Brookside Associates, Ltd.
All rights reserved